Keeping the insulation dry reduces radiation loss and thus saves fuel. Heat loss by radiation from steam pipe to water or wet insulation can be 30 times greater than that to air due to higher thermal conductivity.
For most insulation materials, the minute air cells that get held in a labyrinth or matrix of inert material such as mineral wool, fiberglass or calcium silicate decides the effectiveness of insulation.
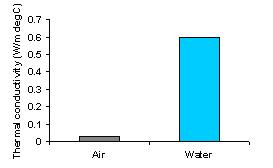
Thermal conductivity is a function of temperature. The thermal conductivity of water is 25 - 50 times that of air. Thus, a waterlogged insulation will lose more amount of heat, thereby adversely affecting the effectiveness of insulation in reducing the radiation losses.
As seen in the graph the thermal conductivity of water at ambient temperature is 0.6 and that of air is 0.025 W/m°C.
Steam lines passing across waterlogged ground or in ducts should be adequately protected from potential damage due to flooding and ingress of rain water.