Ways to prevent fuel wastage when operating industrial boilers
In an ideal world, steam demand would remain constant – and so would boiler operations. But in reality, plants do not operate that way.
Whether it’s due to batch production, production loads, variation across shifts, or seasonally driven production loads, steam demand often fluctuates significantly over the course of a day, week, or month. Despite this, boilers are typically set to run on a fixed configuration. This approach might seem convenient, but is highly inefficient. When a boiler configured for peak performance is made to run at part load without any tuning, it leads to excessive air input, higher stack losses, and suboptimal combustion. This inefficiency builds up over time, resulting in 2–3% higher fuel consumption, sometimes more. And since the equipment appears to be operating normally, the root cause often goes unnoticed.
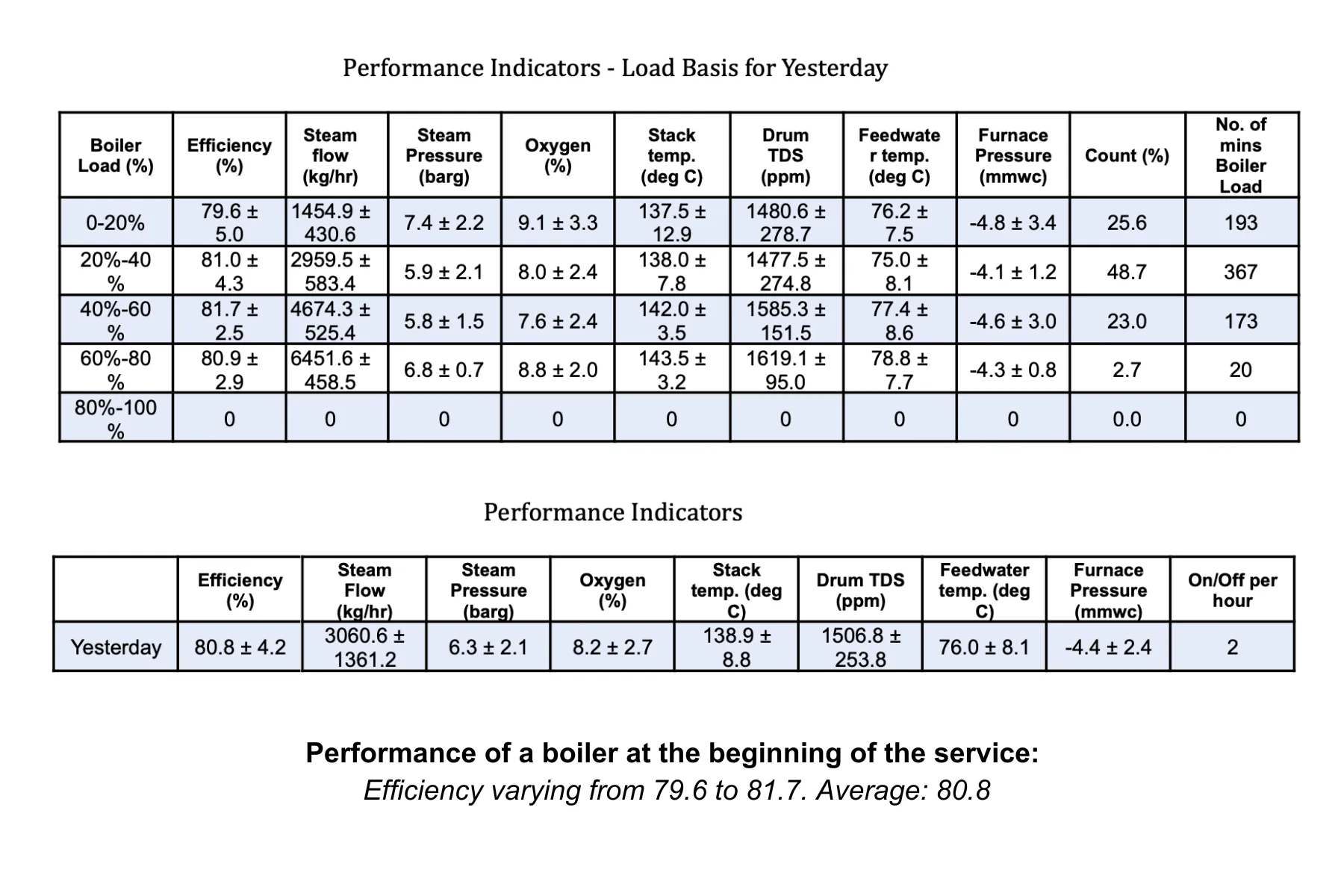
With digital connectivity, tracking operations has made it easier to optimise efficiency. By digitally monitoring your boiler, real-time data is used to flag deviations in performance, including inefficiencies. This means faster corrective action can be taken towards making adjustments for fuel quality and production loads for the day, maximising your steam to fuel ratio.
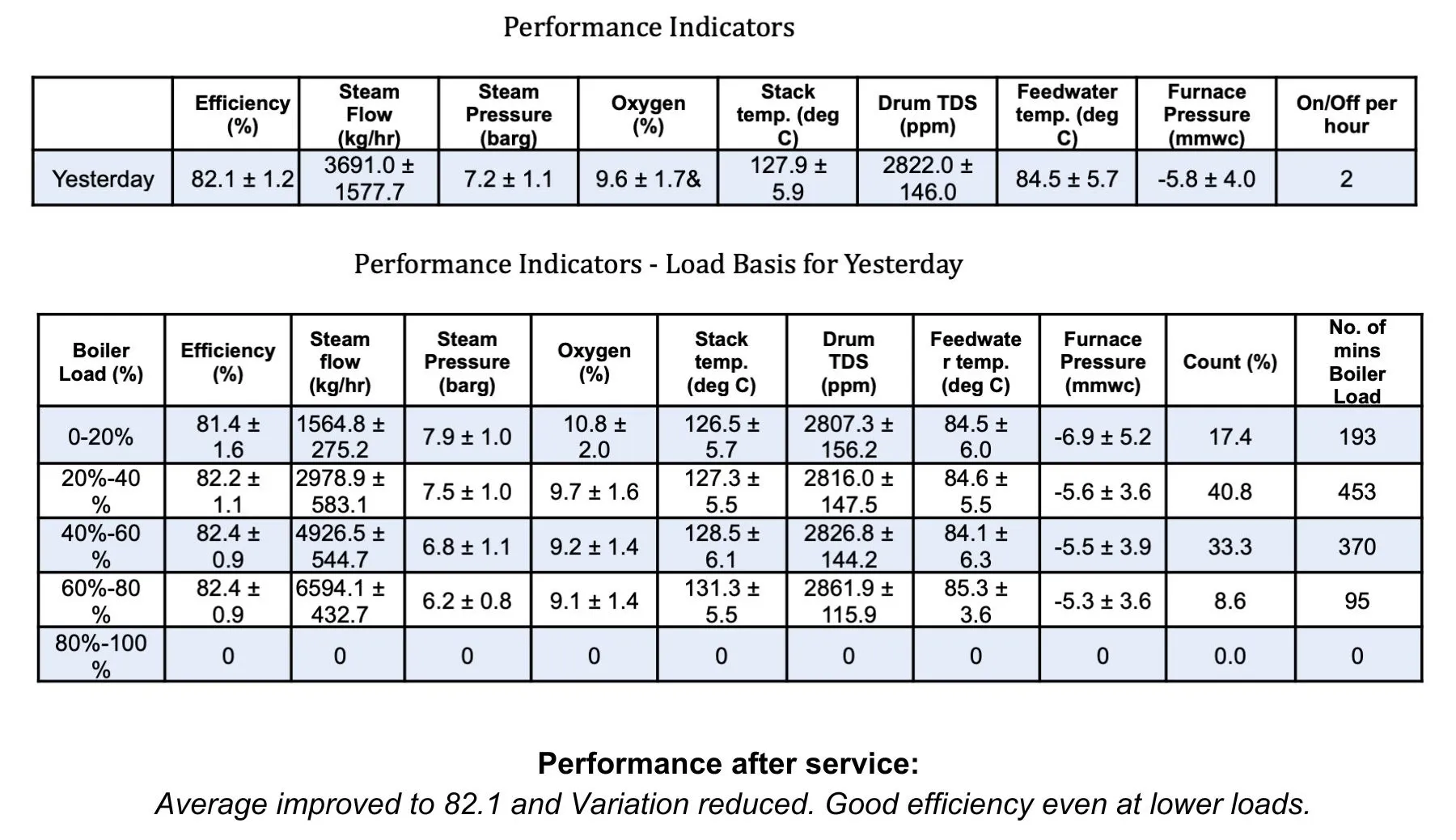
Now, on the flip side, with the increased need/want to digitally connect everything, there is an overwhelming amount of data available. This is where EverSense for Boiler Efficiency, a Forbes Marshall Digital solution, makes actioning the data-driven insights easier. Our EverSense platform provides a dashboard for boiler performance, and flags deviations. Additionally, our specialists identify patterns of fluctuating steam demand and periods where the boiler is operating far from its optimal load point. We provide daily, weekly and monthly reports to your team, highlighting best practices and recommending tailored operating strategies: fine-tuning parameters like air-fuel ratios, burner settings, and modulations for different load conditions.
The result?
Better combustion, improved heat transfer, lower stack temperatures – and crucially, reduced fuel consumption.







