Essential Troubleshooting for Thermodynamic Steam Traps
Thermodynamic steam traps are known for their compact design, robustness, and ability to handle a wide range of pressures, making them a common choice for steam distribution pipelines. They operate on the principles of thermodynamics, relying on the difference in velocity between flash steam and condensate to open and close a disc, discharging condensate intermittently.
While generally low maintenance, these traps can develop specific issues that impact system efficiency. This comprehensive guide, based on expert resources, will help you identify and resolve common problems with thermodynamic steam traps.
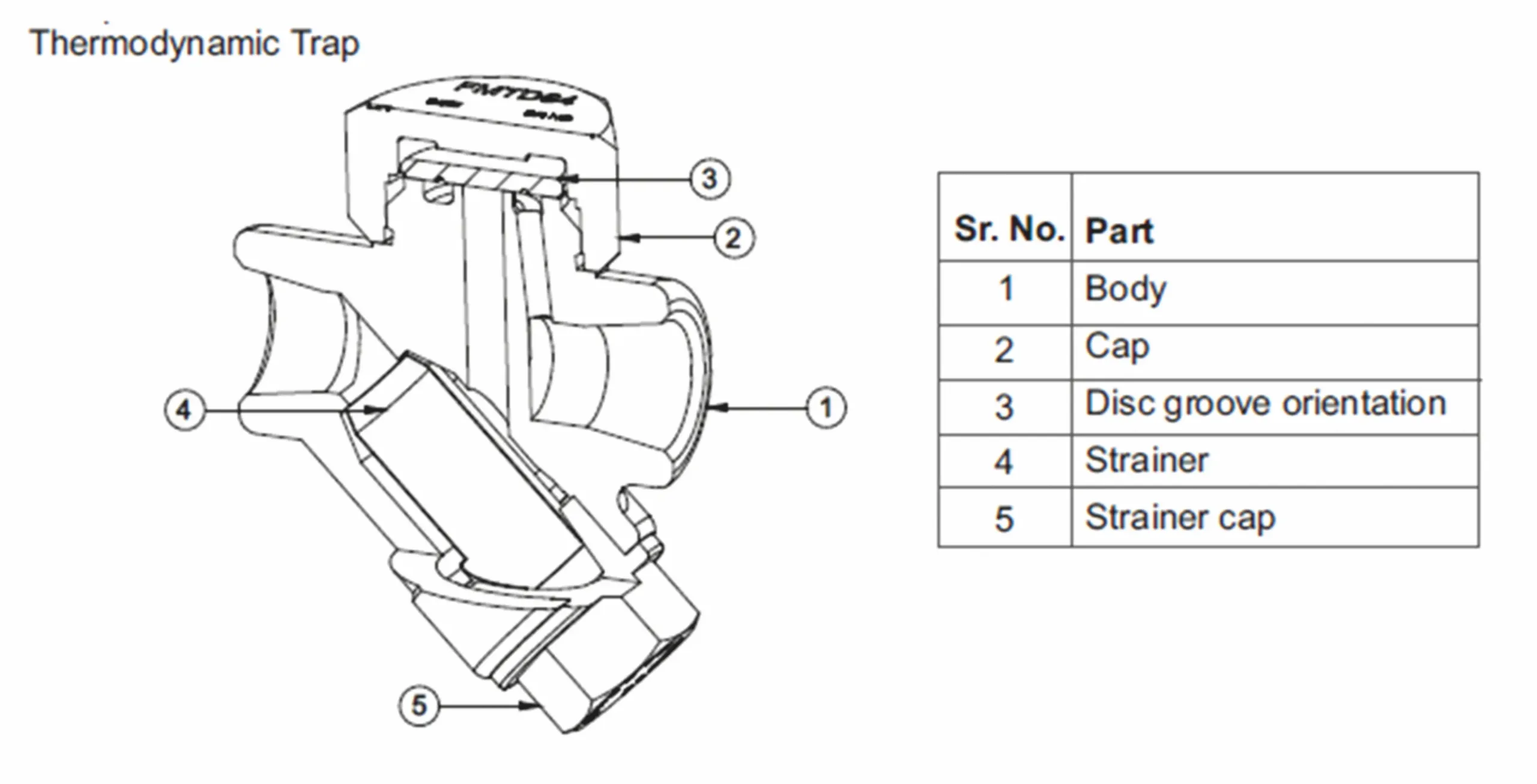
Components of a thermodynamic steam trap
Common Failure Modes in Thermodynamic Steam Traps and How to Fix Them
1. Float Trap Not Discharging Condensate At All
Symptom: The trap feels cold and is not discharging any condensate.
Possible Causes & Recommended Actions:
- Choked Drip Leg or Strainer: The inlet drip leg or the strainer (item 4 in the diagram) is clogged with dirt or debris.
Action: Flush the drip leg and clean the trap strainer. If the strainer screen is rusted or heavily damaged, replace it with a new one.
- Low Differential Pressure: The pressure difference between the inlet and outlet of the trap is insufficient to operate it.
Action: Verify the inlet and outlet pressure of the steam trap. Note that the minimum differential pressure required is 0.25 barg (approximately 3.6 psi).
Symptom: The trap is hot but is not discharging condensate.
Possible Causes & Recommended Actions:
- Air Binding: Air trapped inside the trap prevents the disc from lifting.
Action: Ensure proper air binding of the disc. Sometimes, simply unscrewing the cap (item 2 in the diagram) and screwing it back on tightly can resolve the issue.
- Flash Steam Locked (Trapped): Flash steam may be trapped inside the trap, preventing it from opening.
Action: Pour water on the cap (item 2 in the diagram) of the steam trap to release the flash steam locked inside the trap so it can discharge condensate.
2. Steam Leakage Continuously From The Trap
Symptom: Live steam is continuously observed leaking from the trap.
Possible Causes & Recommended Actions:
- Open or Leaking Bypass Valve: A bypass valve around the trap may be open or leaking.
Action: Ensure that the bypass valve is fully closed. If it’s leaking, repair or replace it.
- Incorrect Installation: The trap might be installed improperly, such as the cap (item 2) not being on top or the condensate flow not aligning with the arrow direction.
Action: Rectify the installation. The cap (item 2) should be on top, and the condensate flow should follow the arrow provided on the trap body.
- Dirt, Debris, Oil Film on Disc or Seat: Foreign material on the sealing surfaces prevents a proper seal.
Action: Clean both the disc and body seat. If required, lap the disc and seat individually.
- Worn Disc or Seat: Normal wear and tear can degrade the sealing surfaces.
Action: If the depth of the scratch is less than 0.25mm, it can be resolved by lapping the disc/seat. Otherwise, replace the disc. Note: The total amount of metal removed from the body seal face should not exceed 0.25mm.
- Disc Stuck in Cap: The disc might be physically stuck within the cap.
Action: Give a light tap to the top of the cap to see if it resolves the problem. If the inner surface of the cap is worn out, replace the cap.
- Excessive Back Pressure: The outlet pressure exceeds the trap’s allowable back pressure limit (typically 80% of inlet pressure).
Action: Ensure the back pressure does not exceed the allowed value.
3. Rapid Cycling
Symptom: The disc of the thermodynamic trap is continuously chattering.
Possible Causes & Recommended Actions:
- Worn Disc or Seat: Significant wear on the disc or seat can cause the trap to open and close too rapidly.
Action: Replace a worn disc with a new one. If the seat is slightly worn, lapping can address the issue. However, in cases of excessive wear, replace the seat or the entire steam trap.
Note: It is important to promptly maintain a steam trap that is rapid cycling, as timely maintenance can prevent excessive wear of the disc/seat.
Ensuring Longevity and Efficiency of Thermodynamic Steam Traps
Regular inspection and maintenance are vital for thermodynamic steam traps to prevent issues like steam loss and ensure optimal system performance. This includes periodic checks of the trap internals and strainers (e.g., quarterly or half-yearly). By addressing these common failure modes promptly, you can significantly improve the uptime and energy efficiency of your steam system
Read next: Troubleshooting for Float Type Steam Traps








